About Class XII Course Syllabus (Code No. 041)
Session 2025-26
The Syllabus in the subject of Mathematics has undergone changes from time to time in accordance with growth of the subject and emerging needs of the society. Senior Secondary stage is a launching stage from where the students go either for higher academic education in Mathematics or for professional courses like Engineering, Physical and Biological science, Commerce or Computer Applications. The present revised syllabus has been designed in accordance with National Curriculum Framework 2005 and as per guidelines given in Focus Group on Teaching of Mathematics 2005 which is to meet the emerging needs of all categories of students. Motivating the topics from real life situations and other subject areas, greater emphasis has been laid on application of various concepts.
Objectives
The broad objectives of teaching Mathematics at senior school stage intend to help the students:
- to acquire knowledge and critical understanding, particularly by way of motivation and visualization, of basic concepts, terms, principles, symbols and mastery of underlying processes and skills.
- to feel the flow of reasons while proving a result or solving a problem.
- to apply the knowledge and skills acquired to solve problems and wherever possible, by more than one method.
- to develop positive attitude to think, analyze and articulate logically.
- to develop interest in the subject by participating in related competitions.
- to acquaint students with different aspects of Mathematics used in daily life.
- to develop an interest in students to study Mathematics as a discipline.
- to develop awareness of the need for national integration, protection of environment, observance of small family norms, removal of social barriers, elimination of gender biases.
- to develop reverence and respect towards great Mathematicians for their contributions to the field of Mathematics.
Class XII (2025-26)
One Paper
Max Marks: 80
| No. |
Units |
No. of Periods |
Marks |
| I. |
Relations and Functions |
30 |
08 |
| II. |
Algebra |
50 |
10 |
| III. |
Calculus |
80 |
35 |
| IV. |
Vectors and Three - Dimensional Geometry |
30 |
14 |
| V. |
Linear Programming |
20 |
05 |
| VI. |
Probability |
30 |
08 |
|
Total |
240 |
80 |
|
Internal Assessment |
|
20 |
1. Relations and Functions (15) Periods
- Types of relations: reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto functions.
2. Inverse Trigonometric Functions (15) Periods
- Definition, range, domain, principal value branch. Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions.
1. Matrices (25) Periods
- Concept, notation, order, equality, types of matrices, zero and identity matrix, transpose of a matrix, symmetric and skew symmetric matrices. Operations on matrices: Addition and multiplication and multiplication with a scalar. Simple properties of addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication. Non- commutativity of multiplication of matrices and existence of non-zero matrices whose product is the zero matrix (restrict to square matrices of order 2). Invertible matrices and proof of the uniqueness of inverse, if it exists; (Here all matrices will have real entries).
2. Determinants (25) Periods
- Determinant of a square matrix (up to 3 x 3 matrices), minors, co-factors and applications of determinants in finding the area of a triangle. Adjoint and inverse of a square matrix. Consistency, inconsistency and number of solutions of system of linear equations by examples, solving system of linear equations in two or three variables (having unique solution) using inverse of a matrix.
1. Continuity and Differentiability (20) Periods
- Continuity and differentiability, chain
rule, derivative of inverse trigonometric functions, like sin-1 x, cos-1 x and tan-1 x, derivative of implicit functions. Concept of exponential and logarithmic functions.
- Derivatives of logarithmic and exponential functions. Logarithmic differentiation, derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms. Second order derivatives.
2. Applications of Derivatives (10) Periods
- Applications of derivatives: rate of change of quantities, increasing/decreasing functions, maxima and minima (first derivative test motivated geometrically and second derivative test given as a provable tool). Simple problems (that illustrate basic principles and understanding of the subject as well as real- life situations).
3. Integrals (20) Periods
- Integration as inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts, Evaluation of simple integrals of the following types and problems based on them.
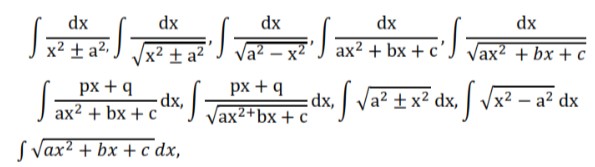
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (without proof). Basic properties of definite integrals and evaluation of definite integrals.
4. Applications of the Integrals (15) Periods
- Applications in finding the area under simple curves, especially lines, circles/ parabolas/ellipses (in standard form only)
5. Differential Equations (15) Periods
- Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation. Solution of differential equations by method of separation of variables, solutions of homogeneous differential equations of first order and first degree. Solutions of linear differential equation of the type:

1. Vectors (15) Periods
- Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines and direction ratios of a vector. Types of vectors (equal, unit, zero, parallel and collinear vectors), position vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a vector, addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Definition, Geometrical Interpretation, properties and application of scalar (dot) product of vectors, vector (cross) product of vectors.
2. Three-dimensional Geometry (15) Periods
- Direction cosines and direction ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian equation and vector equation of a line, skew lines, shortest distance between two lines. Angle between two lines.
1. Linear Programming (20) Periods
- Introduction, related terminology such as constraints, objective function, optimization, graphical method of solution for problems in two variables, feasible and infeasible regions (bounded or unbounded), feasible and infeasible solutions, optimal feasible solutions (up to three non-trivial constraints).
1. Probability (30) Periods
- Conditional probability, multiplication theorem on probability, independent events, total probability, Bayes' theorem, Random variable and its probability distribution, mean of random variable.
MATHEMATICS QUESTION PAPER DESIGN CLASS - XI (2025-26)
Time: 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 80
| S. No. |
Typology of Questions |
Total Marks |
% Weight age |
| 1 |
Remembering: Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers.
Understanding: Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas |
44 |
55 |
| 2 |
Applying: Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. |
20 |
25 |
| 3 |
Analysing :
Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations
Evaluating:
Present and defend opinions by making judgments about information, validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria.
Creating:
Compile information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions |
16 |
20 |
|
Total |
80 |
100 |
1. No chapter wise weightage. Care to be taken to cover all the chapters
2. Suitable internal variations may be made for generating various templates keeping the overall
weightage to different form of questions and typology of questions same.
Choice(s):
There will be no overall choice in the question paper.
However, 33% internal choices will be given in all the sections
Fees
MATHS XI and XII (Same for STATE BOARD & CBSE)
| COMPLETE COURSE |
REVISION
DECEMBER TO FEBRUARY
|
| Rs.14,000/- |
Rs.10,000/- |
Those who register for complete course, they need not pay for revision classes.
Features of the Class
Flexibility
Many programs allow learners to progress at their own pace. This means that they can
spend more time on topics they find challenging and move quickly through areas they
already understand, resulting in a personalized learning experience.
Personal Support
For Personal Support and Individual care,
please contact: +91
9884353569 or
drop an email at atomiceducation4@gmail.com